I cannot cause light; the most I can do is try to put myself in the path of its beam.Photosynthesis in aquatic plants like phytoplankton contributes roughtly 45% of atmospheric oxygen.
― Annie Dillard
Phyto-Phytoplankton are single-celled, aquatic plants adrift and aplenty in the oceans, seas, and freshwater ecosystems. Phytoplankton are microscopic organisms that sustain aquatic animals like whales, shrimp, snails, and jellyfish.
a botanical prefix derived from the Greek phyton meaning plant, flora, or vegetation.
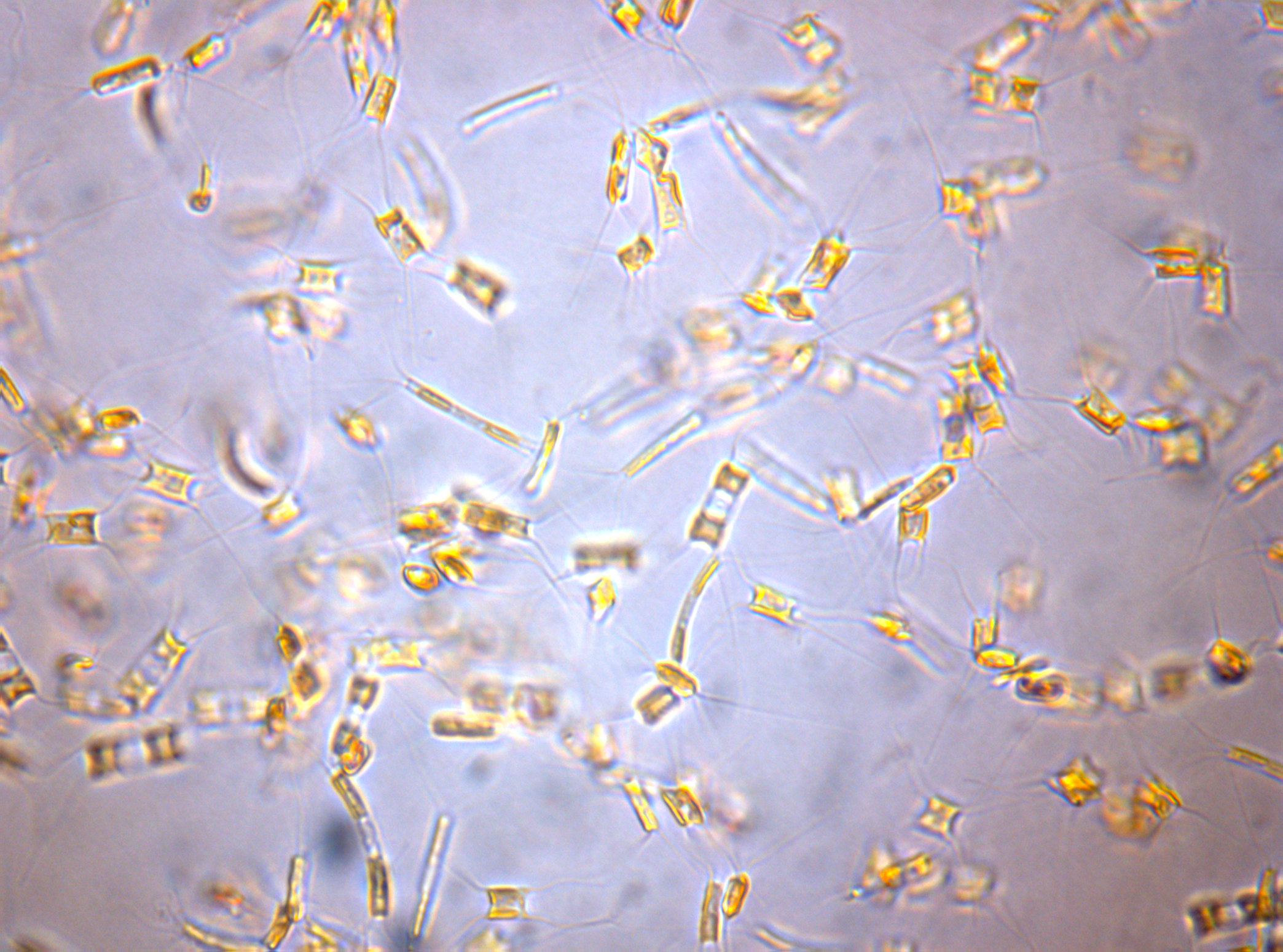 |
| The diatom Attheya Longicornis at 400x magnification |
The main classes of phytoplankton are diatoms and dinoflagellates. Diatoms often form ribbon-shaped colonies, but with no means of propulsion, are subject to the flow of currents.
Dinoflagellates are swimmers with whip-like flagella used to propel themselves.
 |
| Whip-like tail of a dinoflagellate |
All phytoplankton convert the Sun's energy into sustenance via photosynthesis within the euphotic zone. The term euphotic comes from the Greek roots for well lit: εὖ "well" + φῶς "light".
Euphotic ZonePhytoplankton thrive where sunlight can penetrate and fuel their activity. About 90% of all marine life exists in the euphotic zone.
Sunlit water extending from the water's surface to a depth where the light intensity falls to 1% of that at the surface.
The oxygen in today's atmosphere is almost entirely the result of photosynthetic living, which had its start with the appearance of blue-green algae among the microorganisms.
— Lewis Thomas
REFERENCES
- Atmospheric Oxygen, GrokEarth, 18 January 2014.
- Phytoplankton, Wikipedia.
- What are Phytoplankton?, NOAA.

